MARL For Traffic Control
Hey there! Imagine a city where traffic jams are a thing of the past, and the endless chorus of honking horns becomes a distant memory. Inspired by this vision, our trio of passionate minds embarked on a mission to confront a notorious urban challenge: traffic congestion. Our playground? A a multi-agent environment- TrafficJunction, where vehicles transform into AI-driven agents, and algorithms take the driver's seat in redefining traffic norms.
Diving into the world of multi-agent reinforcement learning, we unleashed AI agents onto the canvas of TrafficJunction's virtual streets. Think of these agents as digital drivers infused with algorithmic intuition. Our journey saw us experimenting with various approaches, from the foundational Q-learning and SARSA, to the dynamic potential of deep Q-networks (DQN). Scaling our efforts, we explored DDQN and actor-critic methods, tapping into their technical prowess to address the complexities of urban congestion.
Embark on a journey with us as we harness AI's power to combat traffic congestion, turning city roads into seamless pathways of the future.
02. ENVIRONMENT DETAILS:
We used ma-gym, a collection of multi-agent environments based on openAI gym for this project. The environment is designed in a way that it aims to reduce traffic and number of collisions between vehicles.
Environment used: TrafficJunction4-v1. It is a 4-way junction on a 14x14 grid.
Goal: to reduce traffic jams and number of collisions in a traffic junction.
Rewards: Whenever two cars overlap then a collision occurs. If collision occurs then the agent is penalized with a reward of -10. To prevent traffic jam a reward of -0.01 * τ is given to the agent. τ is the number of time steps taken since the car has arrived.
Actions: There are two possible actions in the environment. Action 0 - Gas. The agent moves forward by one cell. Action 1- brake. The agent stays in the same cell.
Observation space: The state of each agent is a vector with (3^2) *(|n| + |l| + |r|) dimensions. The variables n,l,r represent the one-hot representation of the agent’s id, current location of the agent and the assigned route number. There are two versions of the environment: V0 - Each agent gets its own local observation. V1 - Each agent gets the local observation of every other agent.
Episode terminates when all the agents reach the goal position or when the number of timesteps in an episode exceeds the max_timesteps(40).
03. Implementation Details
In this project, we introduced a multi-agent algorithm designed to untangle the urban chaos. Imagine a symphony of algorithms orchestrating vehicles' movements to eliminate traffic snarls and minimize accidents. Our toolbox was loaded with versatile strategies: classic Tabular algorithms like Q-learning and SARSA, coupled with the neural might of deep Q-networks (DQN), DDQN, and the intelligence of actor-critic methods. Curious about our secret sauce? We cracked open the door to our training environment, revealing the base configuration that powered our experiments: Discount factor: 0.99 Learning rate: 0.2 Number of Episodes: 1000 Gamma: 0.99
At first, a lone agent faced the challenge across all algorithms. The promising outcomes spurred us on, leading us to the next level: two agents for each algorithm. These agents shared local observations, sparking a leap in learning efficiency. Surprisingly, our results were so optimistic that we stuck to the existing reward function, skipping the need for tweaks.
04. Results
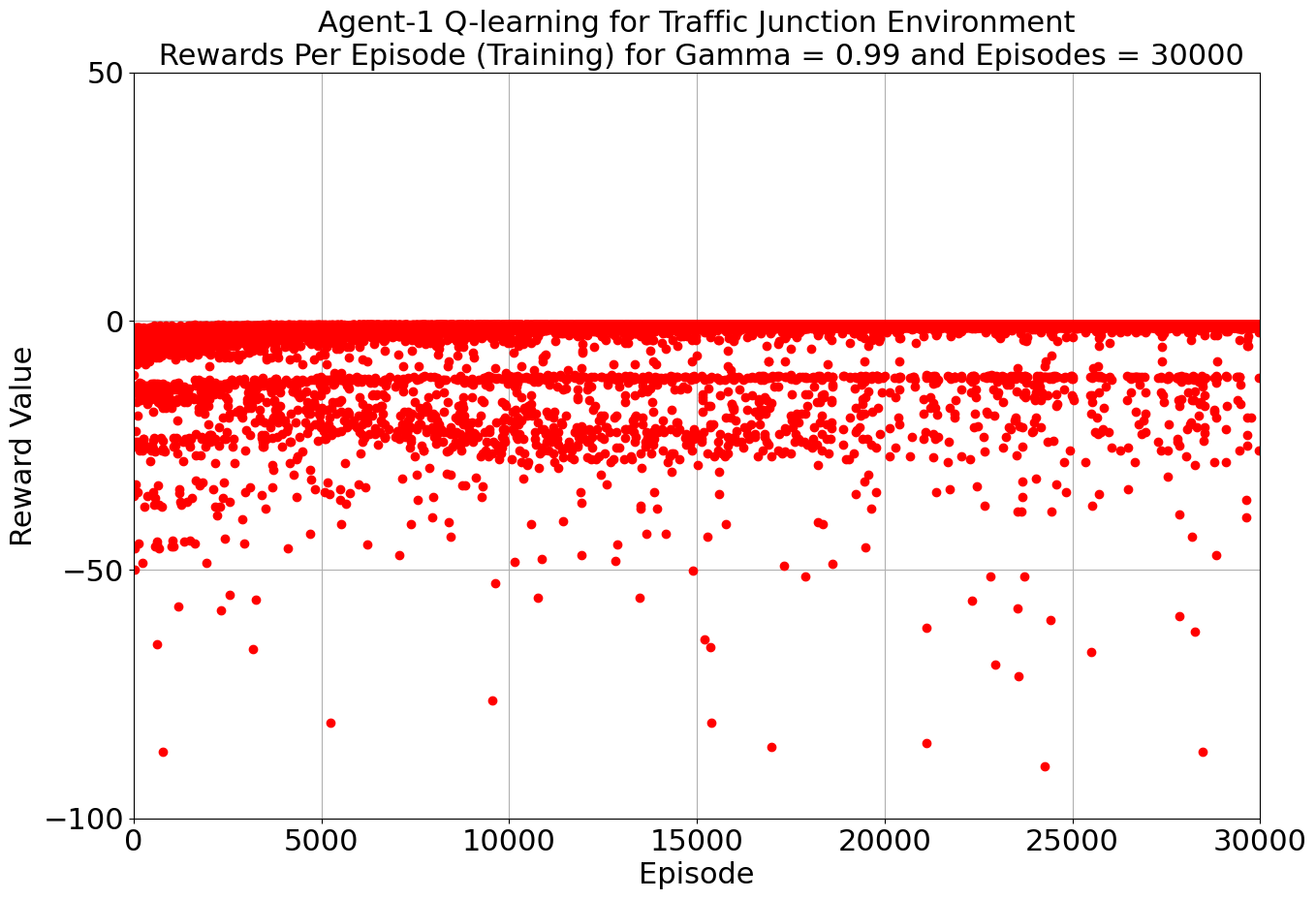
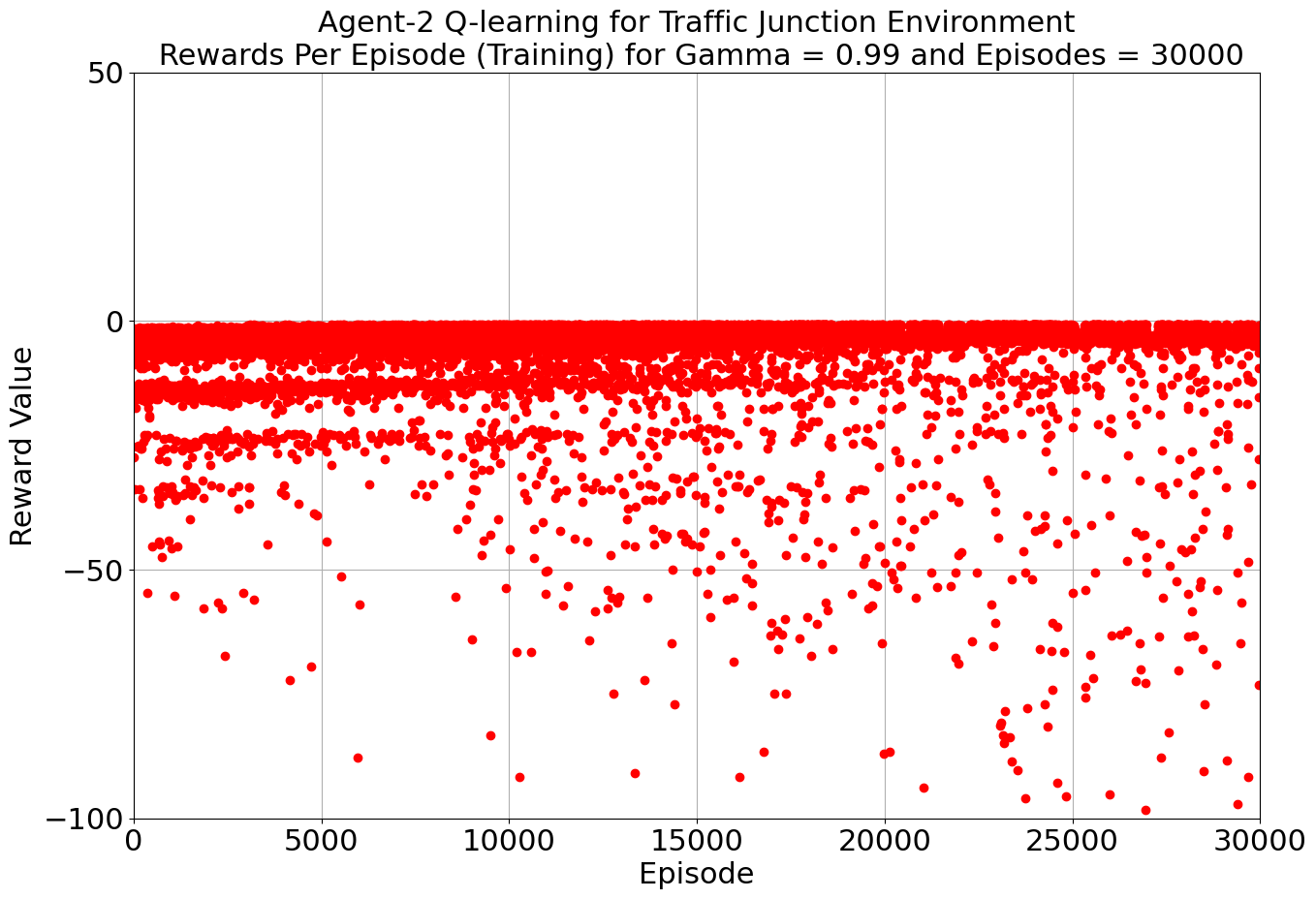
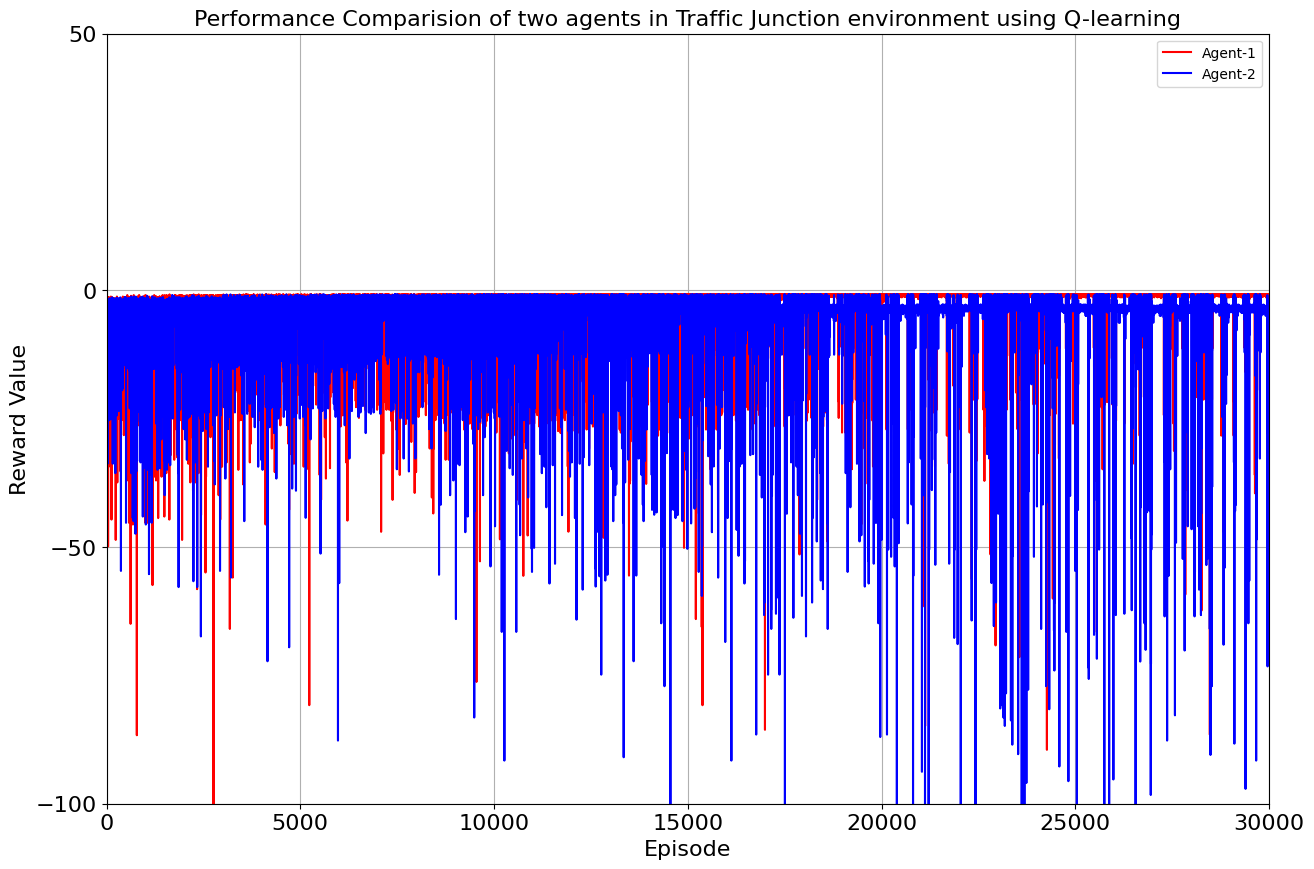
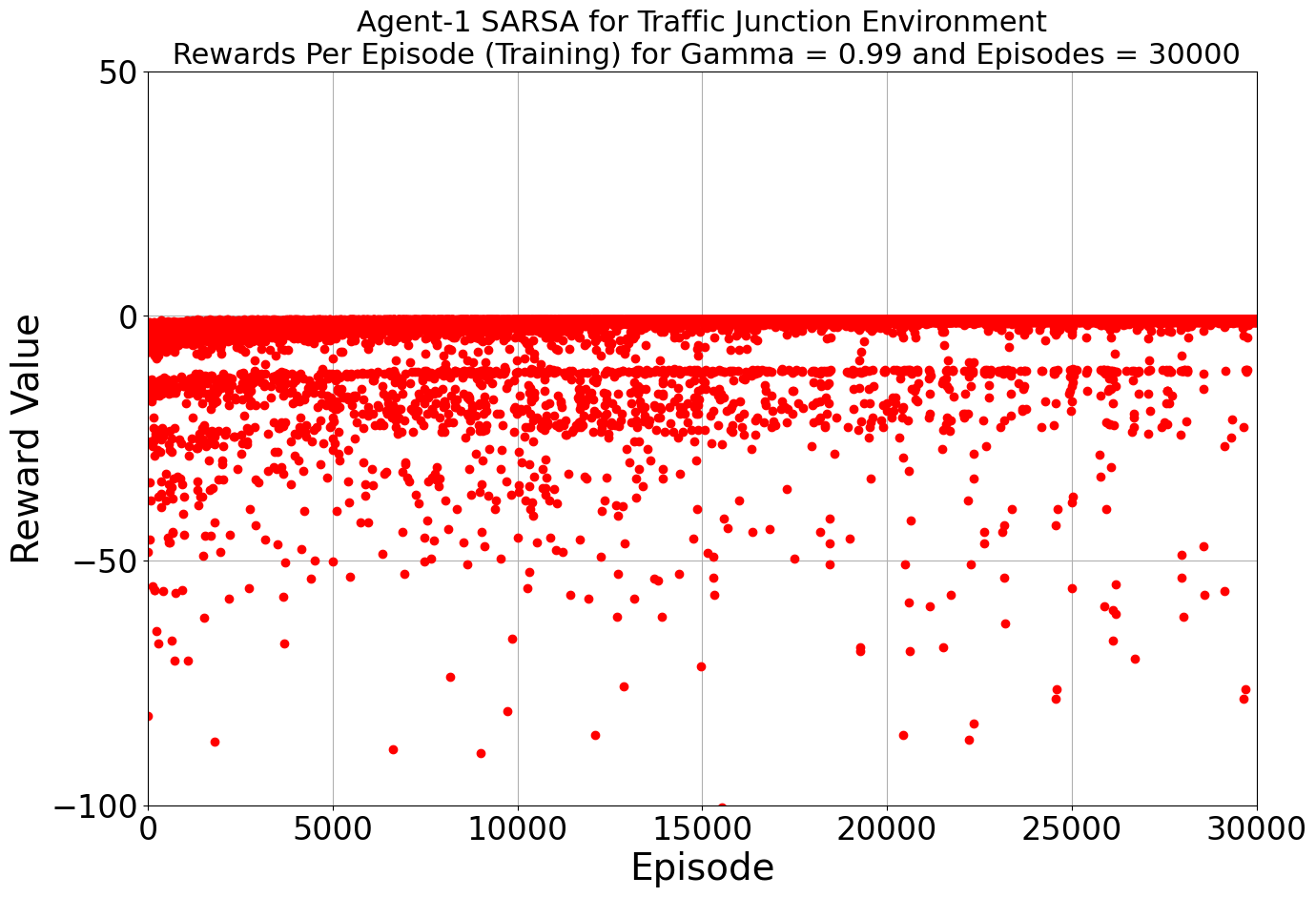
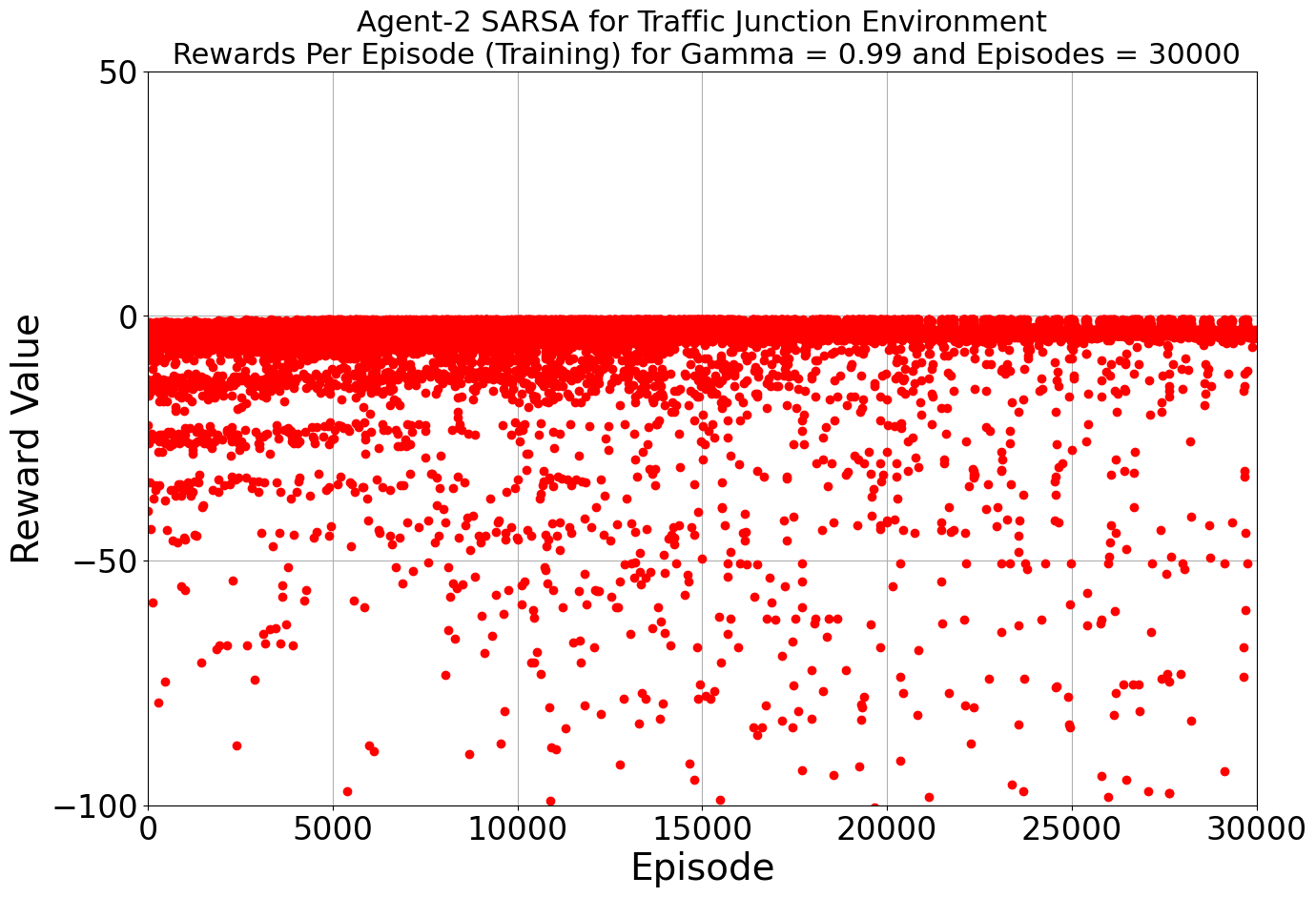
Our journey into the realm of AI-driven traffic solutions began with a determined step: harnessing the power of Q-Learning and SARSA. Armed with a learning rate of 0.2 and a gamma value of 0.99, our algorithms embarked on their training, turning our multi-agent environment into a digital battleground against congestion and accidents.
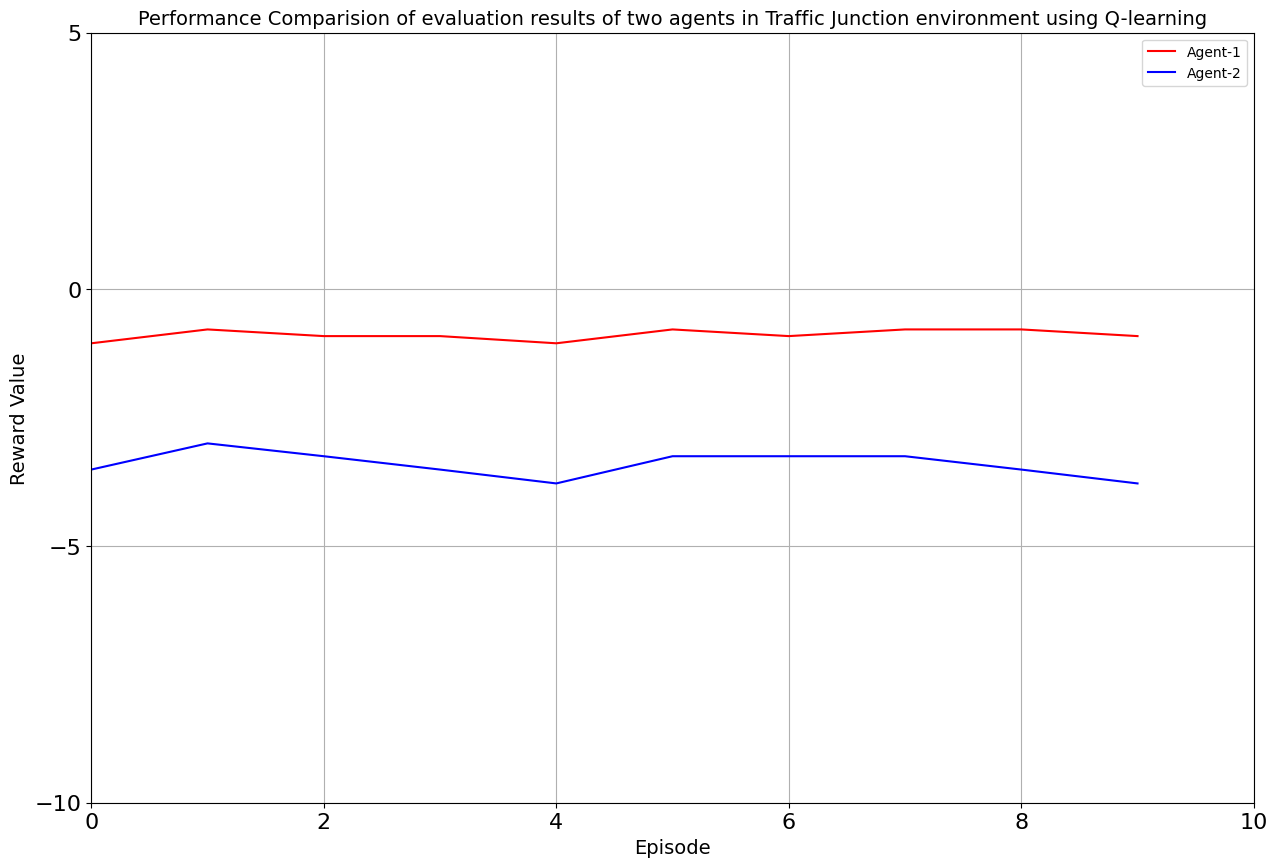
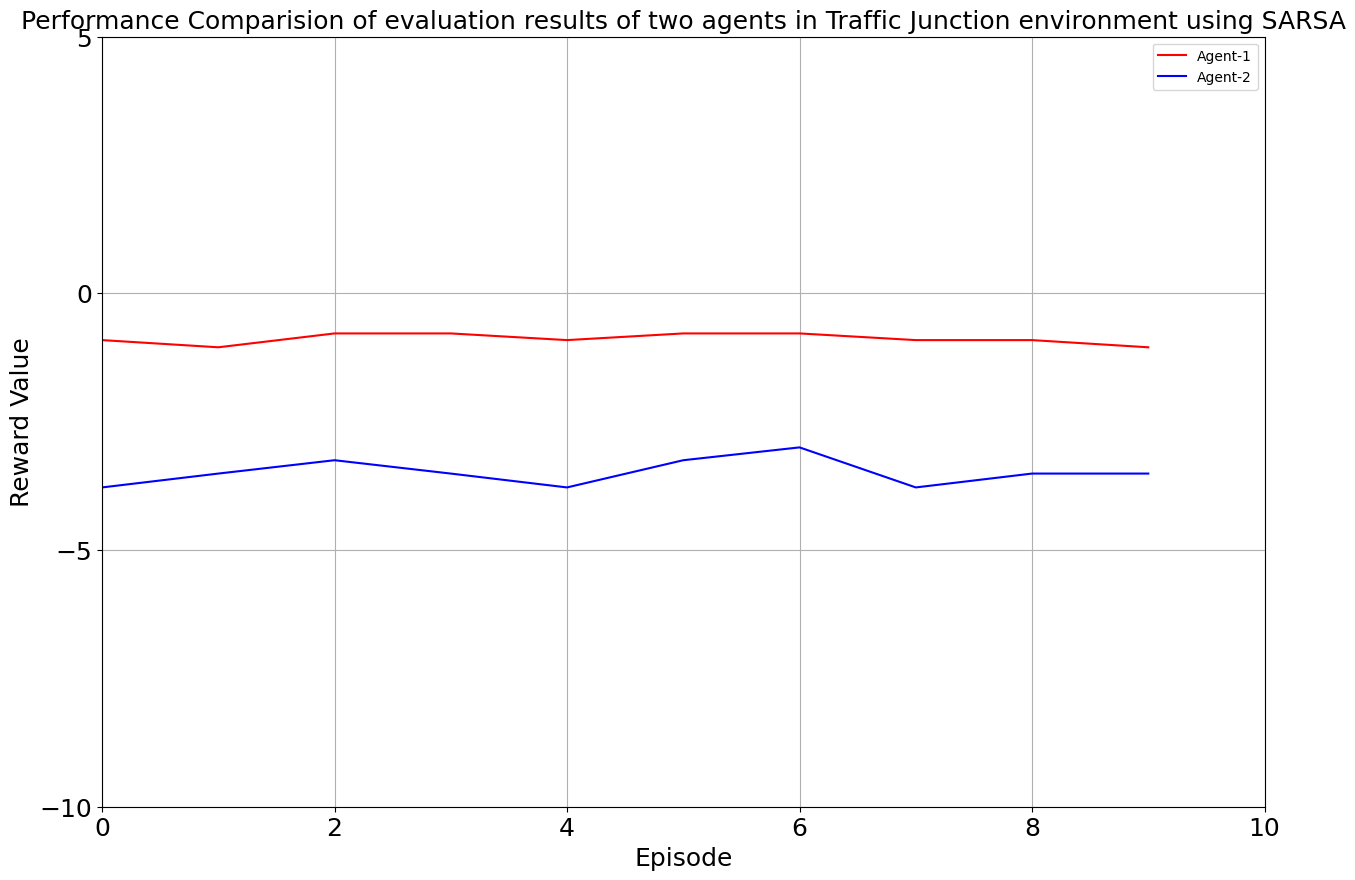
As the iterations unfolded, our environment flourished under the tutelage of Q-Learning and SARSA. The results were promising, with both algorithms showcasing their prowess. The average reward spoke volumes: -0.886 for Agent 1 and -3.409 for Agent 2 in the Q-Learning corner, and -0.886 and -3.487 for the two agents in the SARSA realm. A glimpse into the efficiency of each algorithm, laying the groundwork for what was to come.
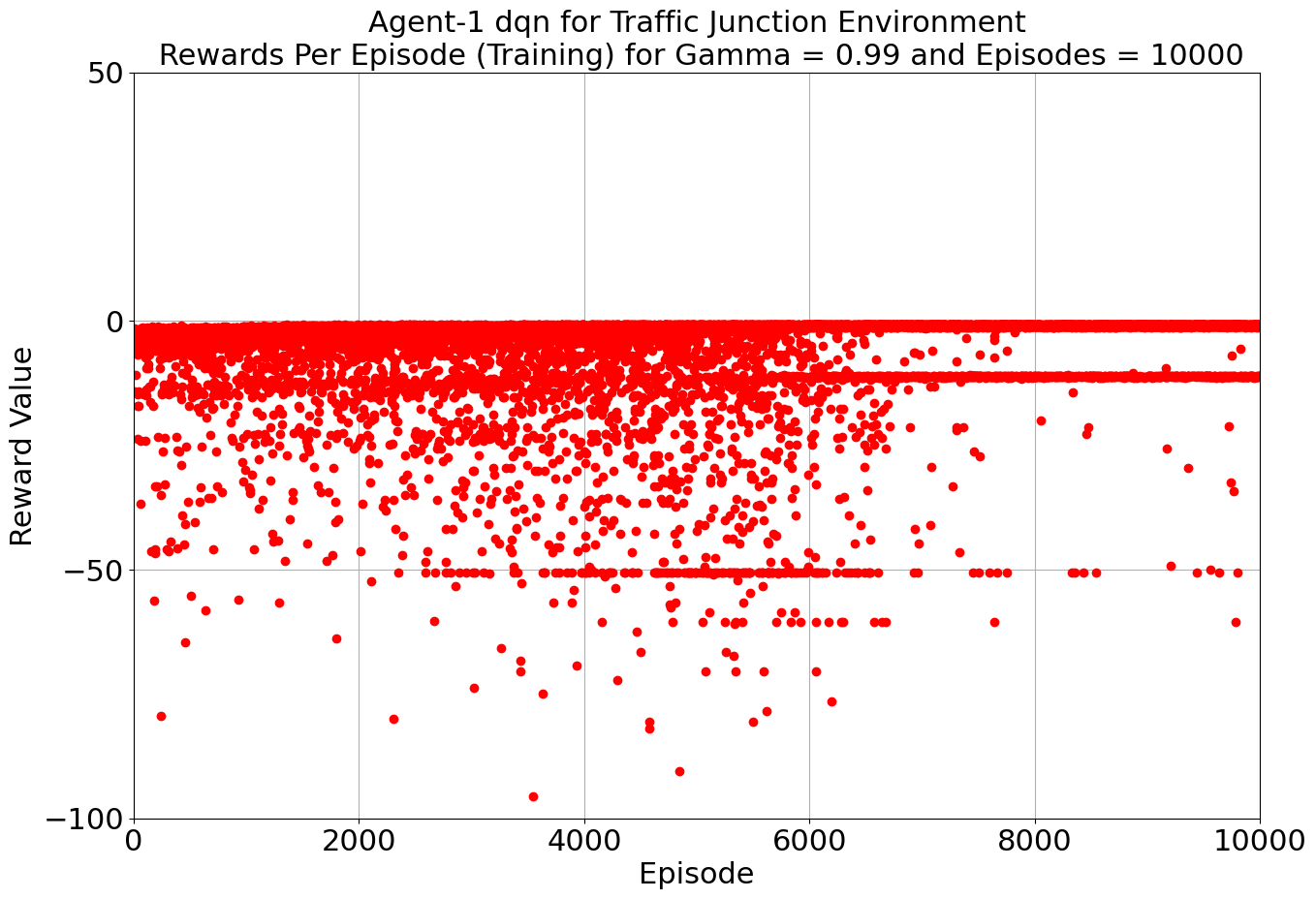
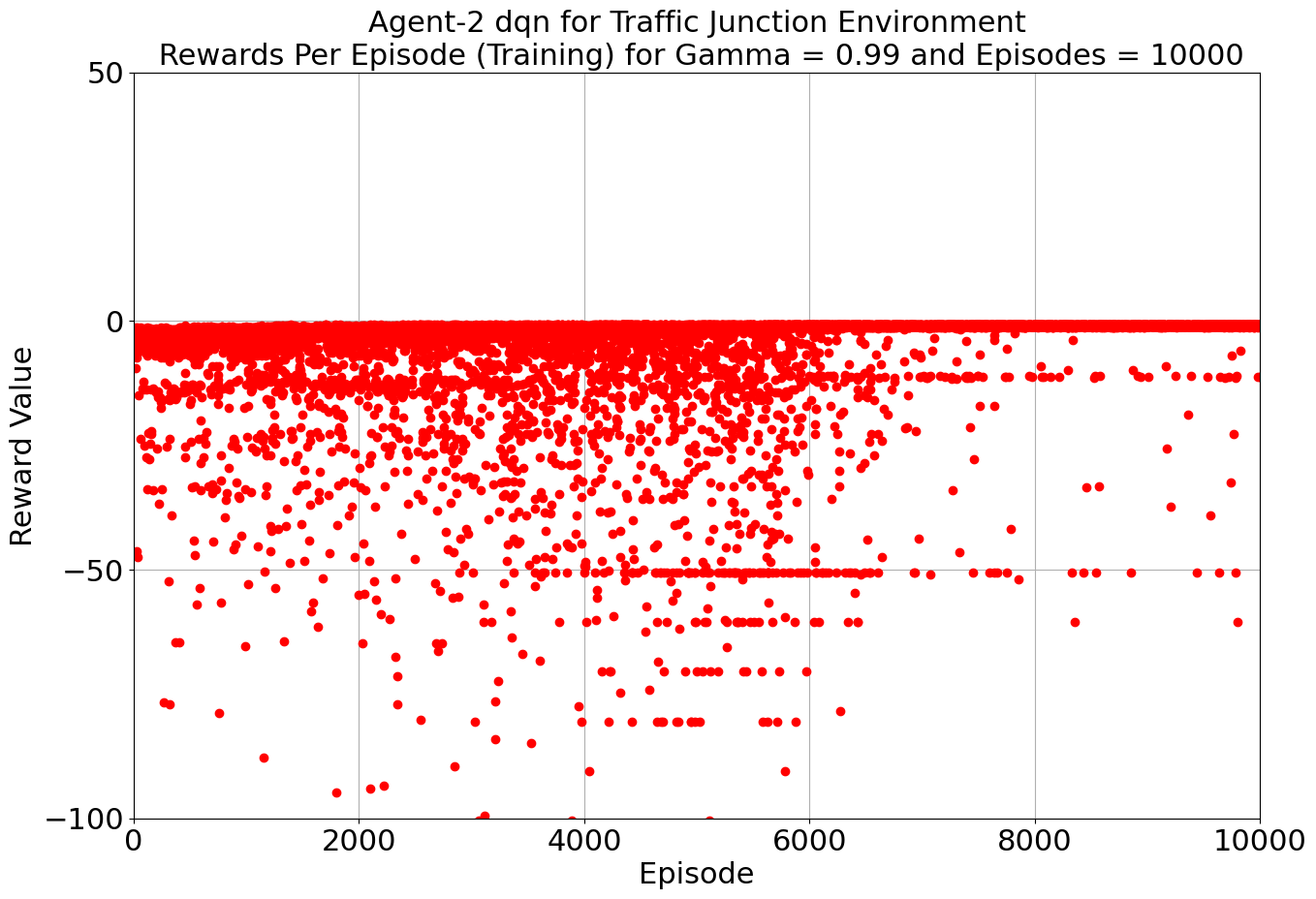
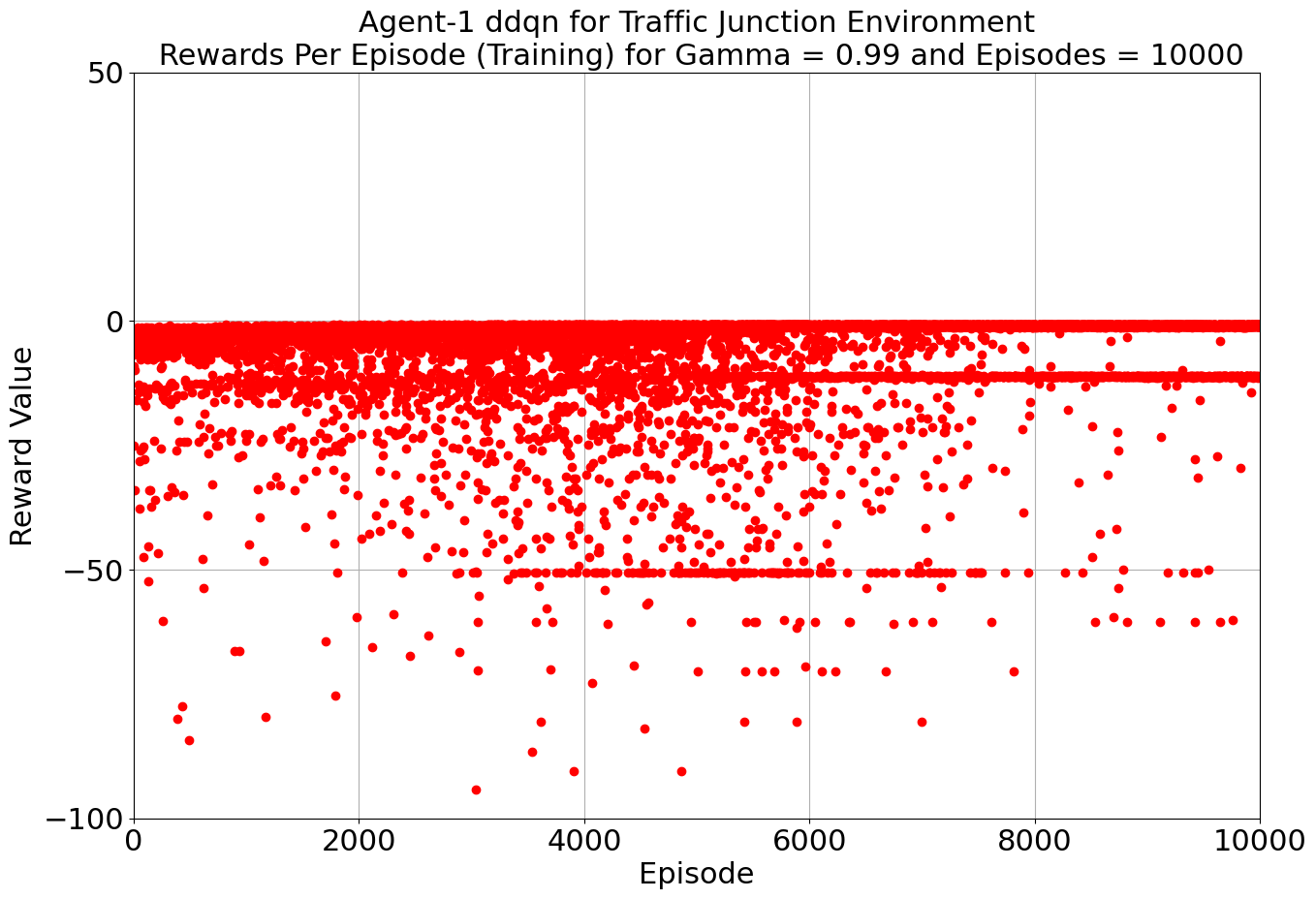
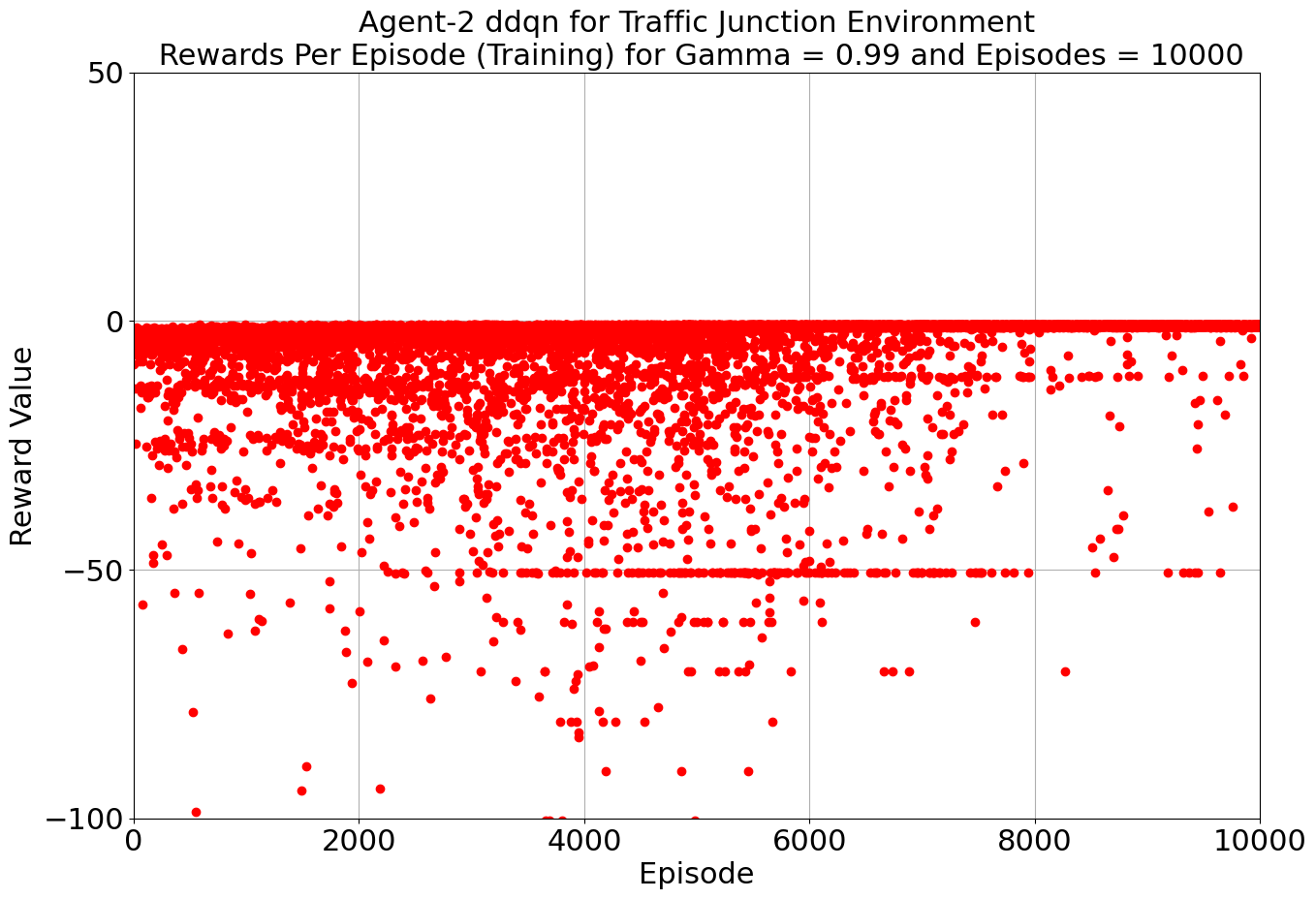
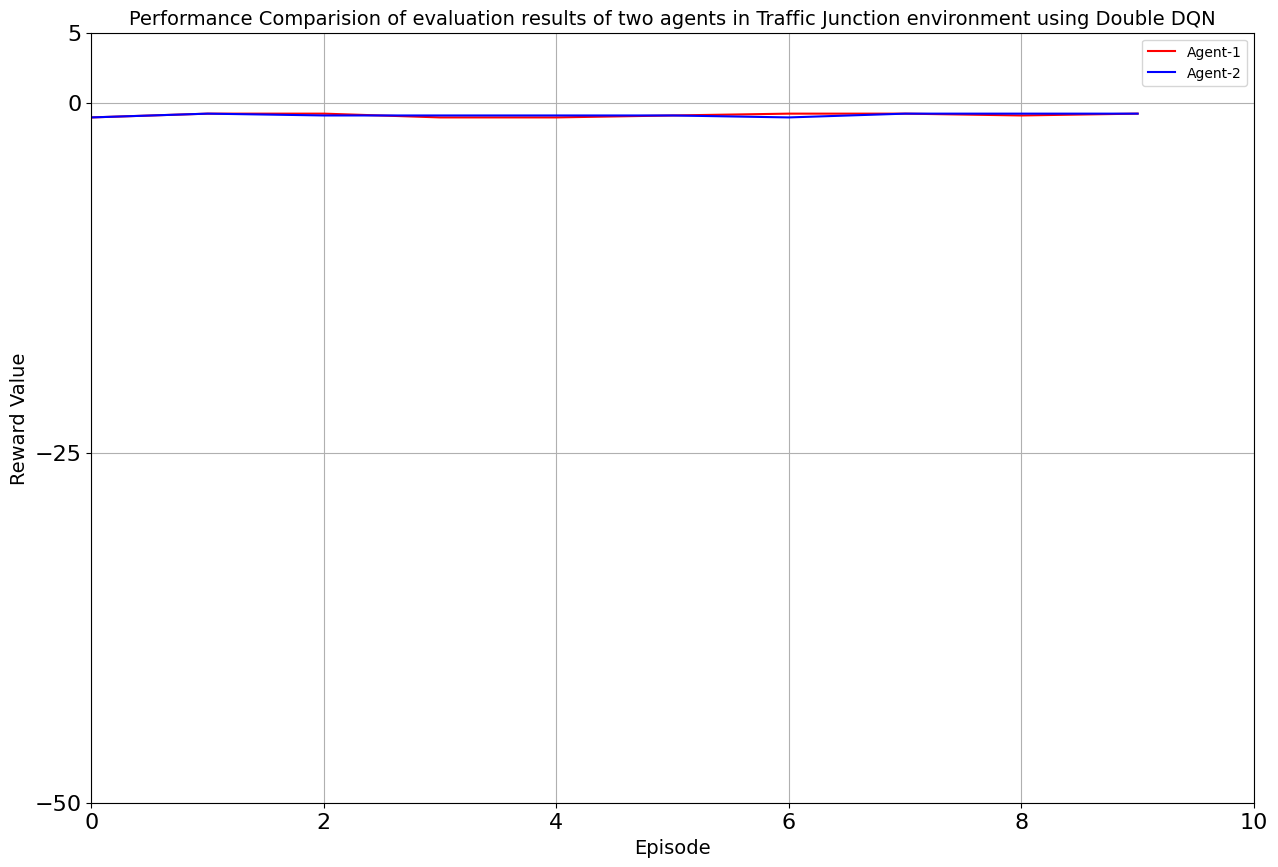
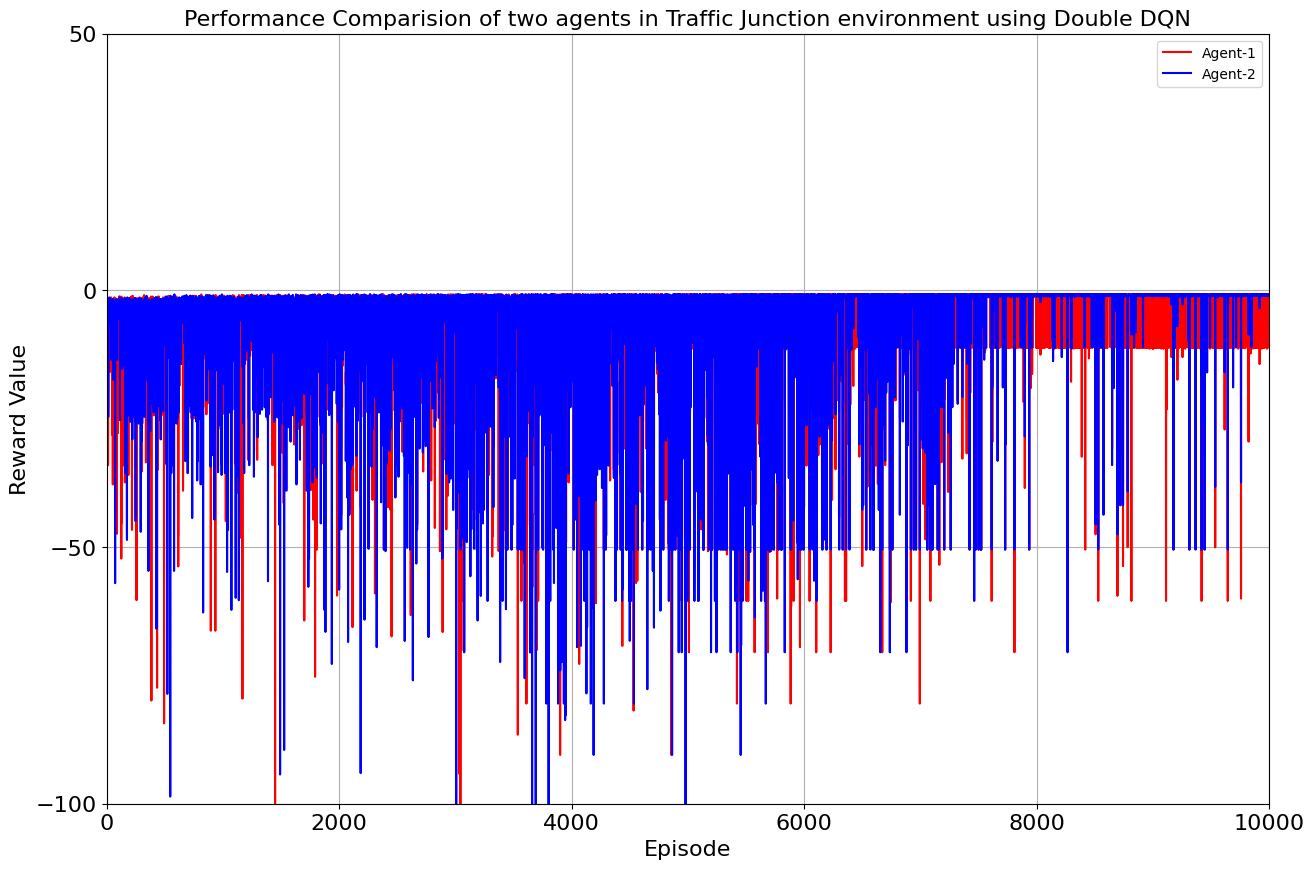
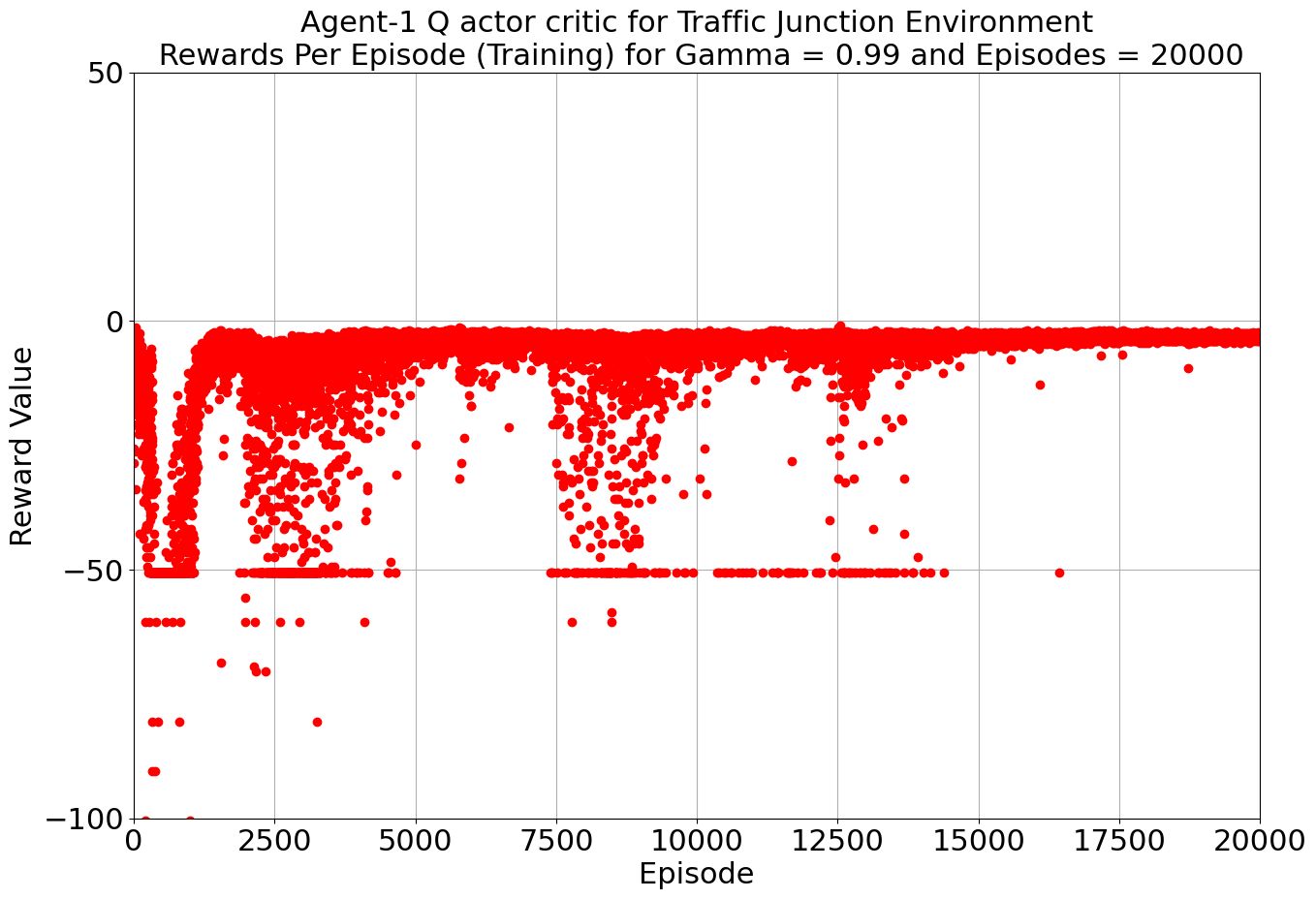
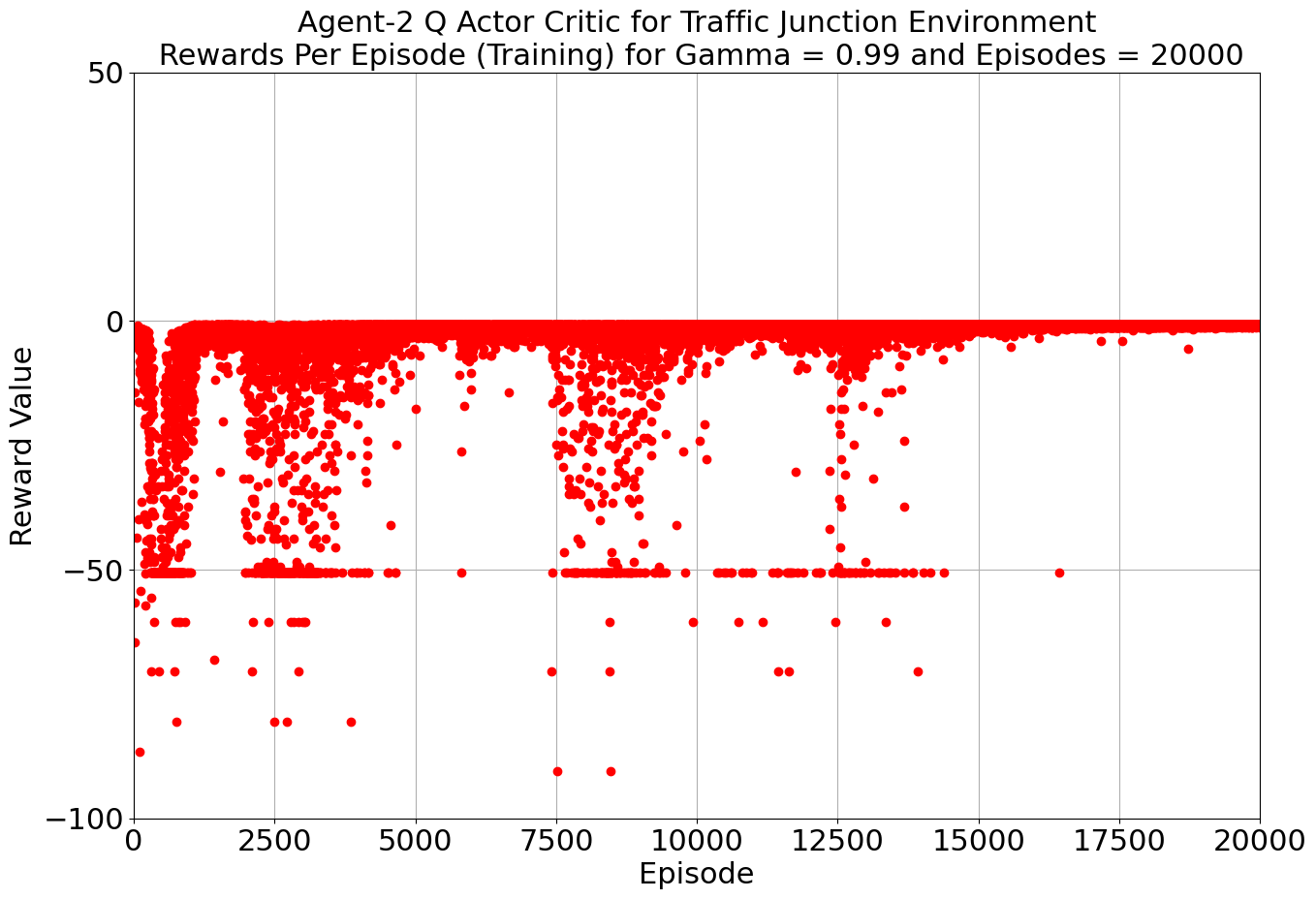
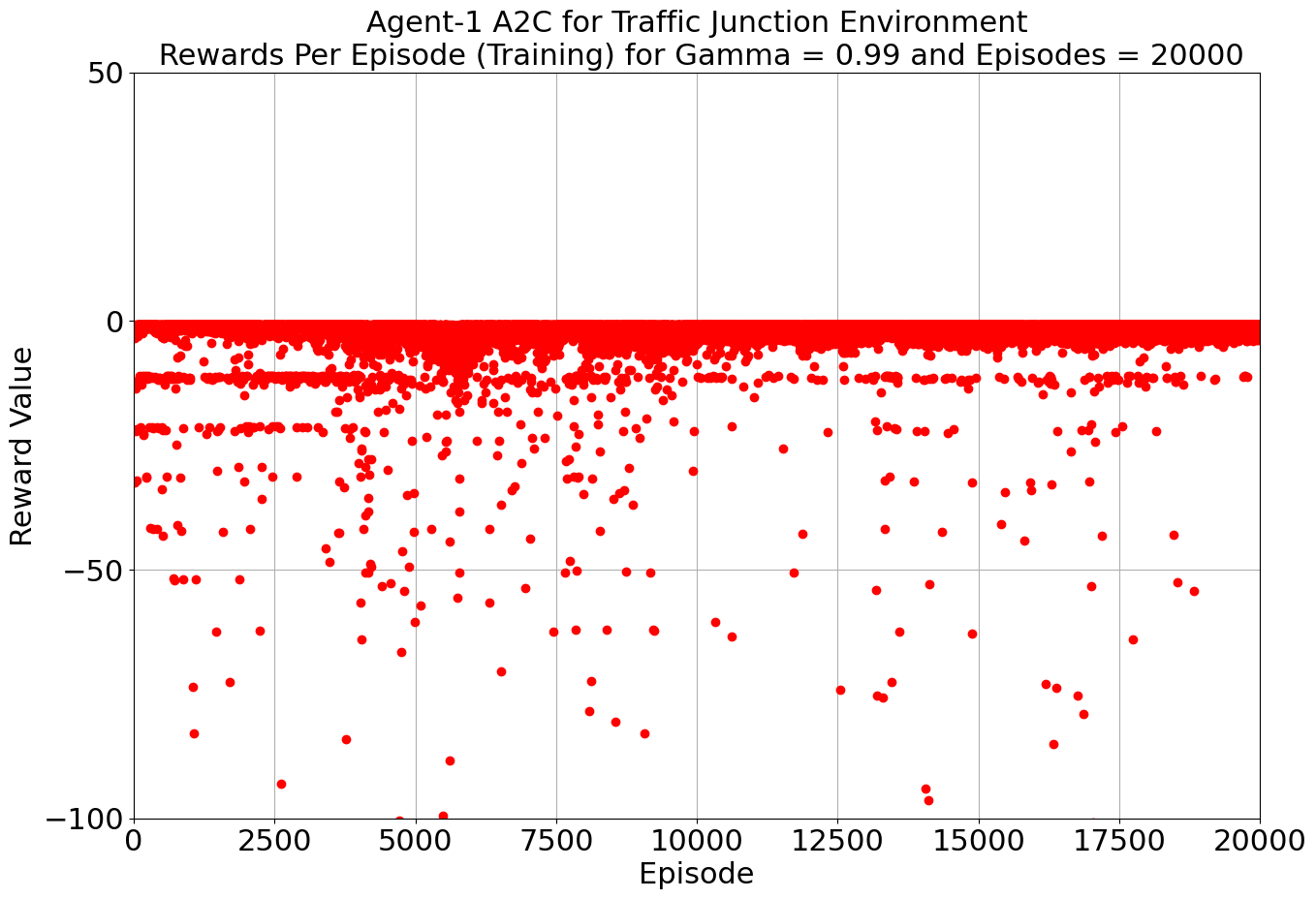
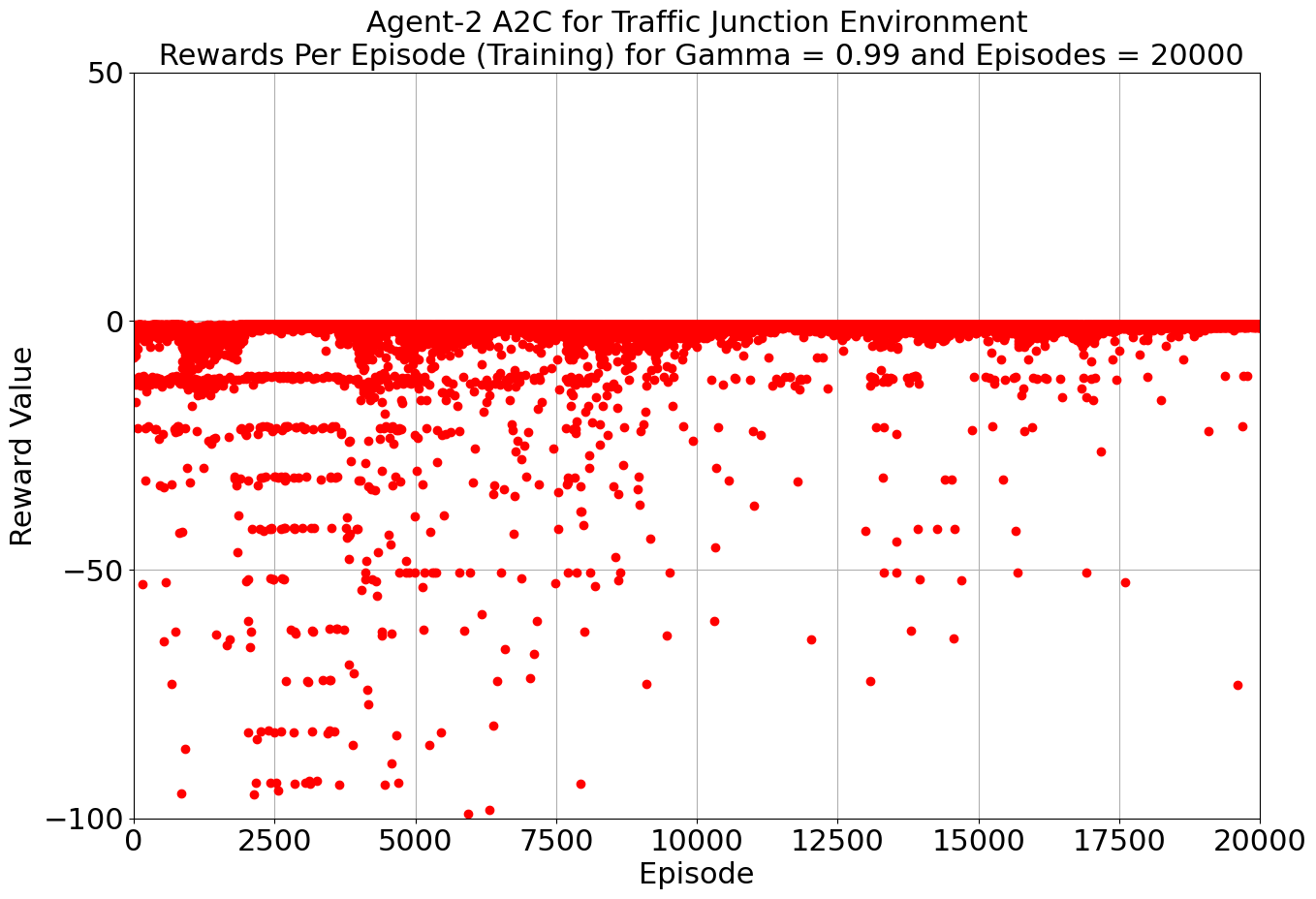
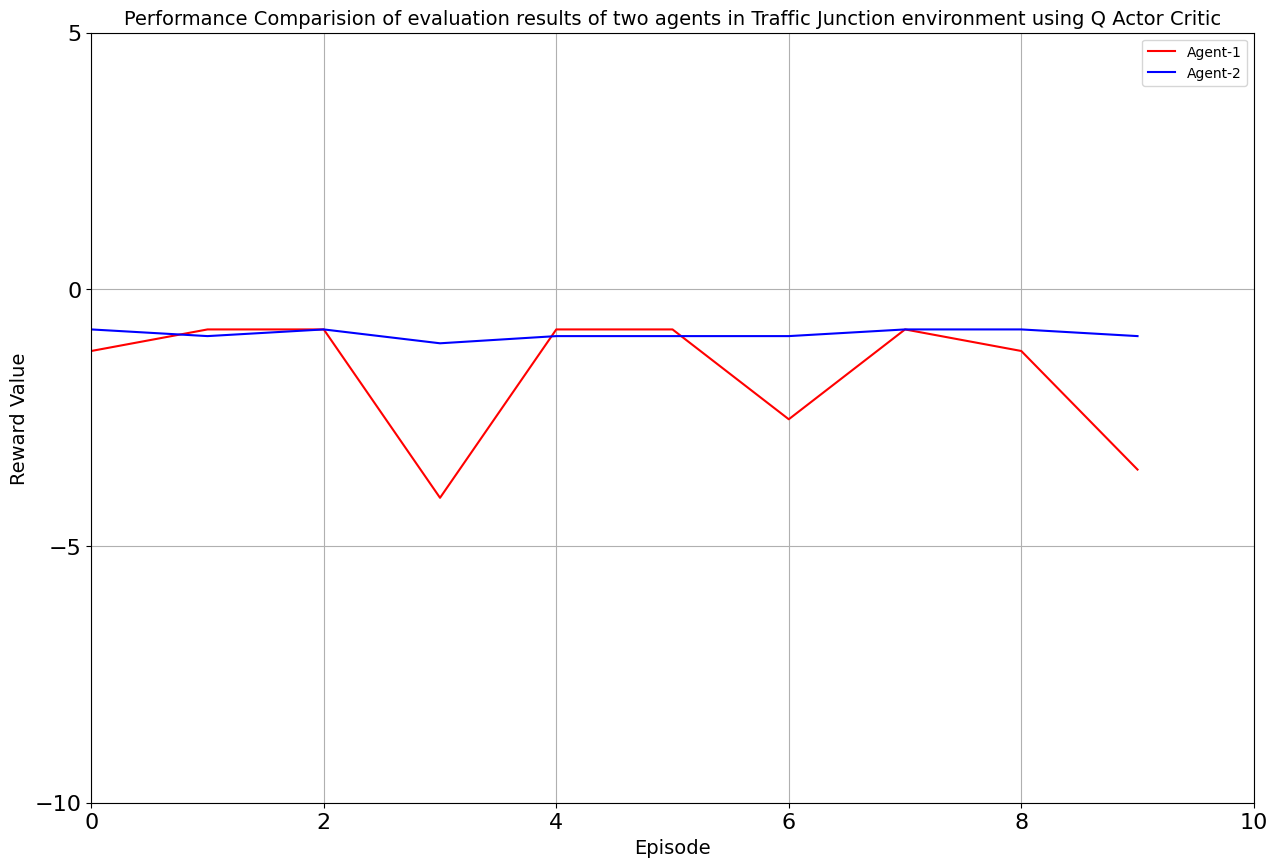
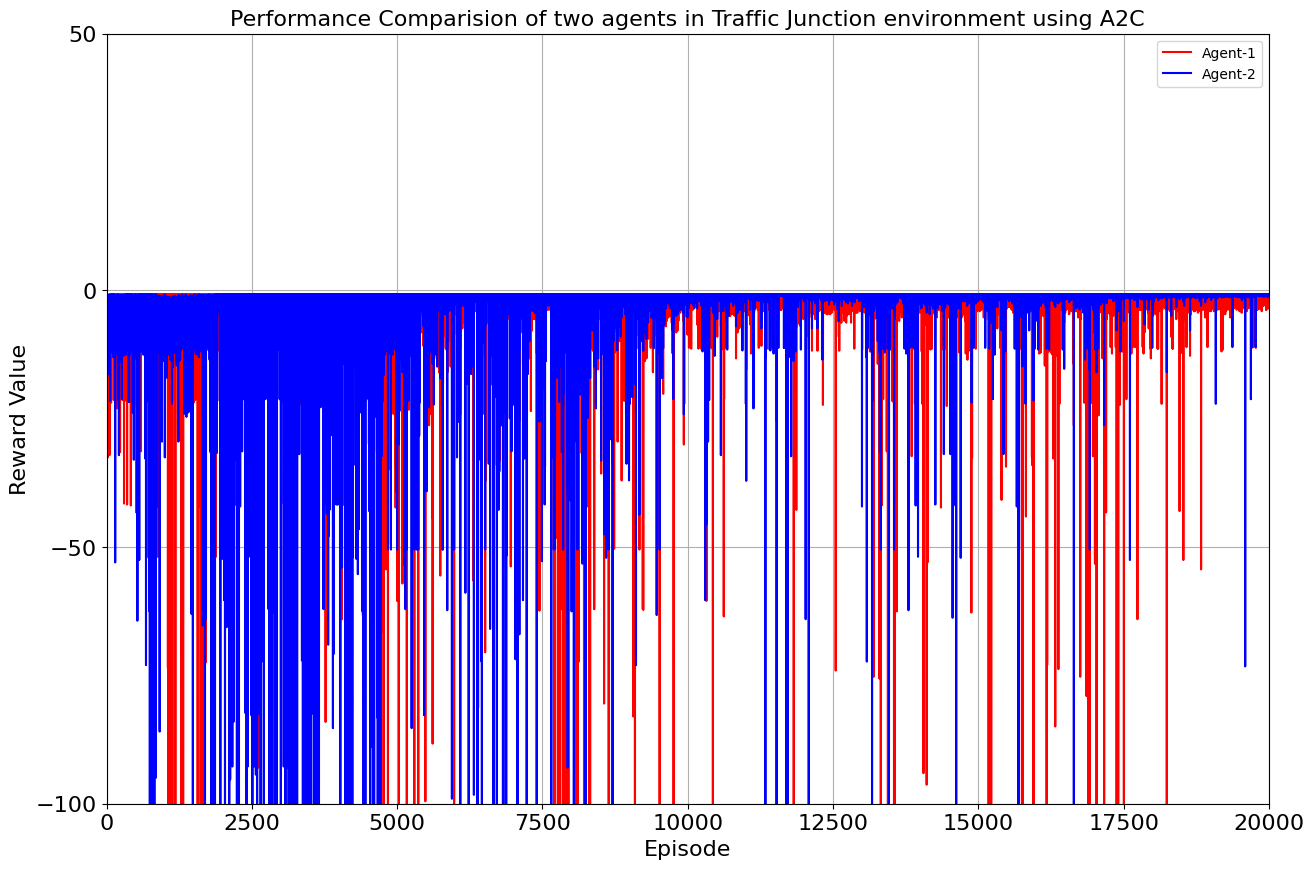
Our toolkit expanded as we ventured into the world of DQN, Double DQN, Q Actor Critic, and Advantage Actor Critic. The arena was set, and the challenge was real. DQN and Double DQN embarked on a 10,000-episode journey, relentlessly working towards convergence. On the other side, Q Actor Critic and Advantage Actor Critic chose the path of patience, spanning 20,000 episodes each to unearth their potential.
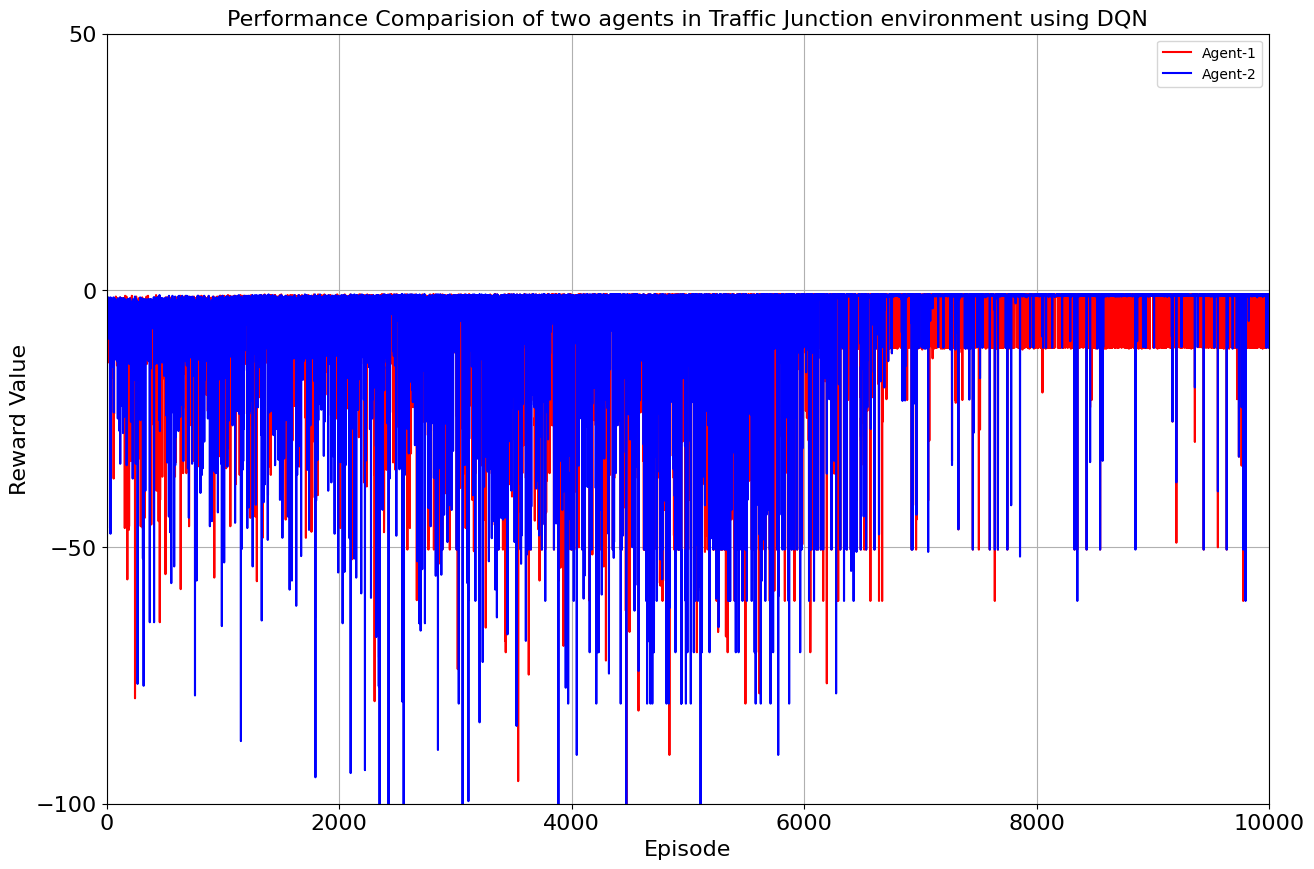
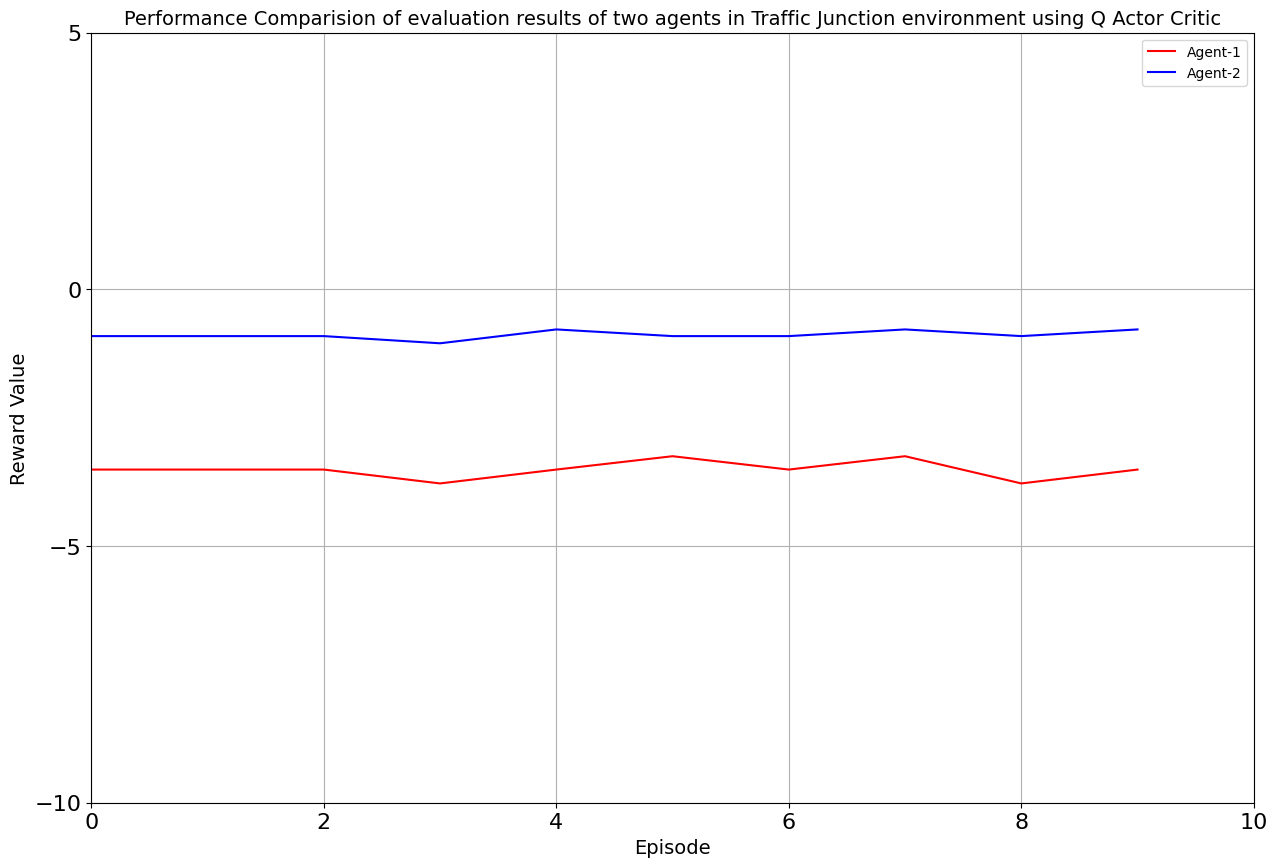
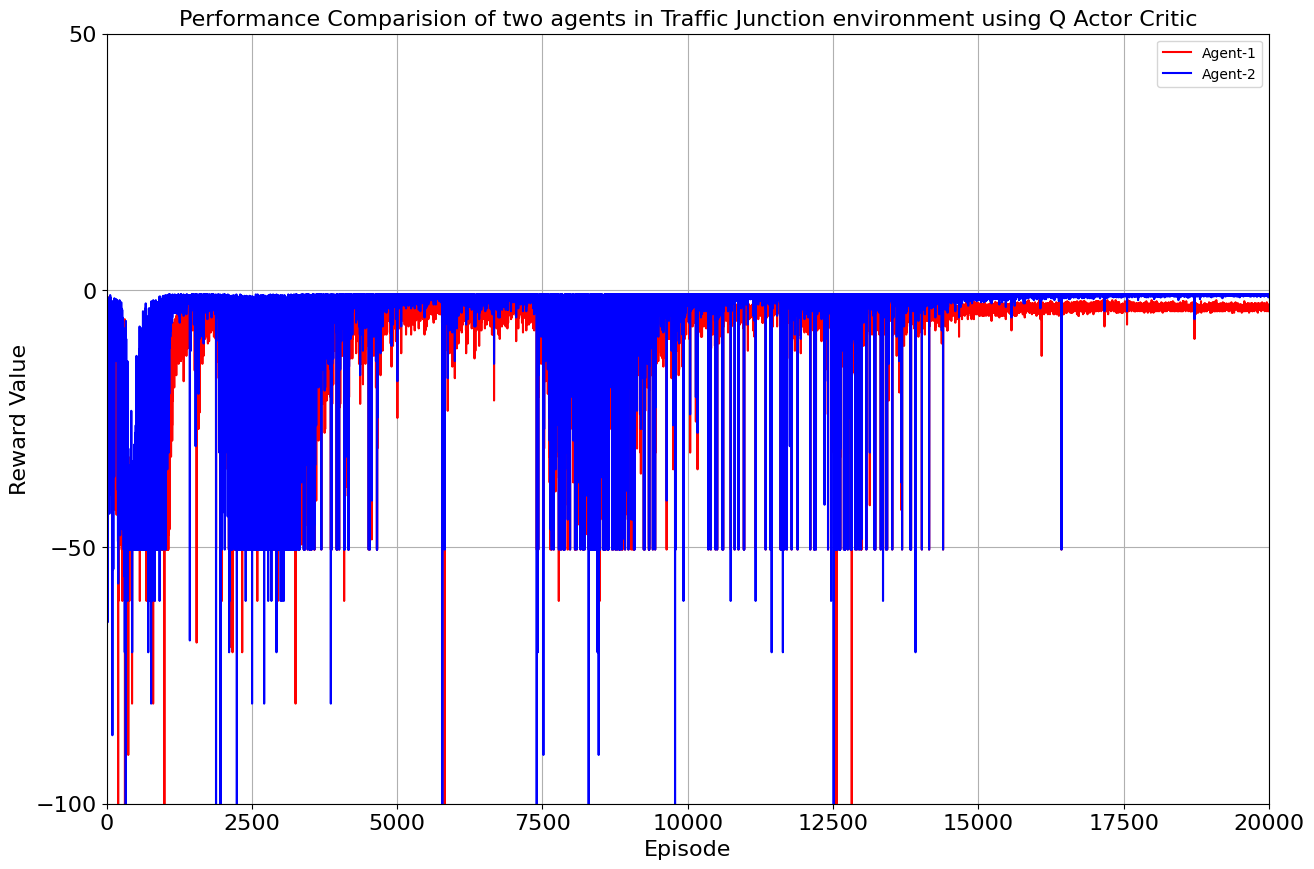
Drumroll, please! The moment of truth arrived as we unveiled the average rewards achieved by each algorithm. DQN and Double DQN stood tall, showcasing their prowess after conquering their 10,000-episode trials. Q Actor Critic and Advantage Actor Critic proved their mettle through dedication, emerging triumphant after 20,000 episodes. The culmination of our efforts, as average rewards whispered tales of progress, learning, and the ever-improving landscape of AI-powered traffic solutions. Join us as we dive deeper into the algorithms' victories and lessons learned, unraveling the intricate dance between code and creativity that drove us toward a future where traffic woes bow down to AI's strategic prowess. Average reward for each algorithm is as follows:
| Algorithm | Number of episodes trained | Agent 1 average reward | Agent 2 average reward |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q-Learning | 30000 | -0.886 | -3.409 |
| SARSA | 30000 | -0.886 | -3.487 |
| DQN | 10000 | -0.913 | -0.967 |
| DDQN | 30000 | -0.887 | -0.885 |
| Q-Actor Critic | 20000 | -3.51 | -0.885 |
| Advantage Actor Critic | 20000 | -1.64 | -0.872 |